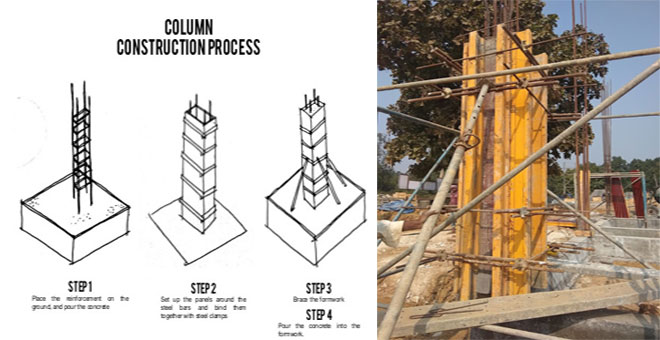
Column Construction Steps At Site
Column construction is a crucial aspect of any structural project. Columns play a vital role in transmitting the load from the slab and beams to the underlying soil. Proper construction of columns ensures the stability and durability of the entire structure. In this article, we will discuss the step-by-step process of column construction at the construction site.
Types of RCC Column depending on Shapes
Before diving into the construction process, it's essential to understand the different types of RCC columns based on their shapes. This classification helps in achieving specific architectural and structural requirements. The two primary types of RCC columns based on shapes are:
- Circular Columns: Circular columns are often used for uncovered exteriors, providing an elegant architectural view.
- Square or Rectangular Columns: Conventionally, square or rectangular columns are used for any structure.
ALSO READ : VIDEO TUTORIALS FOR CIVIL ENGINEERS
Types of RCC Column Depending on Length
The length of a column also affects its design and construction. Based on the length-to-width ratio, RCC columns can be classified as:
- Short Columns: Short columns are considered when the height-to-width ratio (L/B) is less than or equal to 12. In most cases, a floor height of 3 meters or 10 feet results in the provision of short columns.
- Long Columns: When the height of a floor exceeds 3 meters or 10 feet, it is necessary to verify the L/B ratio. If the ratio is greater than 12, long columns are required. Designing long columns requires careful consideration of various forces that are produced.
Types of RCC Column depending on moments
RCC columns can also be classified based on the moments they experience. The two main types are:
- Biaxial Columns: Biaxial columns are designed to handle axial loads and moments in two directions. They are commonly used in building corners.
- Uniaxial Columns: Uniaxial columns are designed to handle axial loads and moments in one direction. They are often used as side and internal columns.
Understanding the different types of RCC columns helps in selecting the appropriate construction method and reinforcement techniques.
Construction Process of RCC Columns
The construction process of RCC columns can be divided into the following four phases:
1. Column layouts - The first step in column construction is determining the layout of the columns. This involves placing ropes in the grid lines and labeling the position of columns. Accurate column layouts are essential for the overall structural integrity of the building.
2. Column Reinforcement Work - Column reinforcement is a critical step to ensure the strength and stability of the columns. The following points should be considered during the reinforcement work:
- Verify the number and diameter of vertical bars.
- Determine the spacing between vertical bars.
- Calculate the development length based on the diameter of the bar.
- Ensure proper lapping of alternate bars at the same height.
- Avoid providing lapping inside beams or slabs.
- Provide lapping at l/3 or 2l/3 of the column, as per structural notes.
- Determine the spacing for stirrups according to the drawing.
- Bend the hooks of stirrups at precise angles.
- Verify the corner of the stirrups, ensuring they are perfectly tied with binding wire.
3. Column Formwork
Formwork is essential to provide support and shape to the columns during the concrete pouring process. Proper column formwork ensures accurate alignment and prevents any deformation. Consider the following points during the column formwork:
- Ensure the columns are aligned vertically to transmit the load effectively.
- Use adequately strong formwork to withstand the pressure of fresh concrete.
- Secure the formwork in position throughout the concreting process.
4. Pouring of Concrete
The final phase of column construction is the pouring of concrete. This step must be executed with precision to achieve a strong and durable column. Consider the following points during and after the concreting process:
- Determine the appropriate method of concrete placement, whether manual or with the aid of a machine or pump.
- Use machine-mix concrete for smaller quantities and ready-mix concrete (RMC) for larger quantities.
- Confirm with the client if the concrete should be placed using a pump or by hand.
- Pour the concrete up to the slab bottom, and the remaining column concreting should be performed during the pouring of the slab and beam.
- Utilize a mechanical vibrator to ensure proper compaction of each layer. Avoid excessive vibration, as it can lead to segregation of the concrete.
- Aim for a target slump of 160 mm.
- Pour the concrete from a height not exceeding 1.5 meters to prevent segregation.
- Avoid construction joints in the column.
- Maintain the proper cover as per the structural drawings.
- Keep the temperature below 30 degrees Celsius during concrete pouring.
- After pouring and vibrating the concrete, carefully examine the horizontality and verticality of the column.
Conclusion
Proper construction of RCC columns is essential for the stability and longevity of any structure. By following the step-by-step process discussed in this article, builders and engineers can ensure the successful construction of columns at the construction site. Understanding the different types of RCC columns and their requirements is vital to achieve the desired architectural and structural goals.