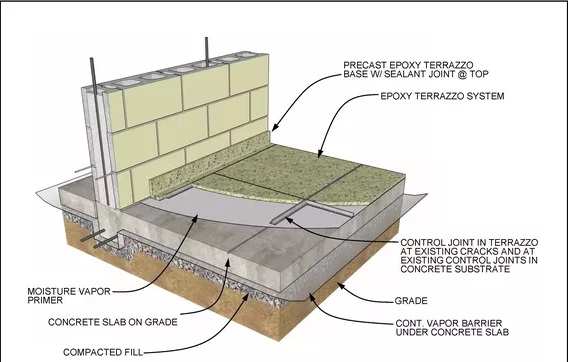
Detail information about slab on grade
Slab-on-grade alias floating slab foundations belong to a structural engineering practice whereby the concrete slab that will perform as the foundation for the structure is developed from a mold set into the ground. The concrete is then set into the mold, providing no space among the ground and the structure.
Slabs on grade belongs to pavements not usually structural components.
- Pavements transmit loads via compression to supporting soil.
- So long as the deformations of soils are low, little bending occurs in the slab.
Slabs on grade are regarded as successful when there exist little or no cracking.
Types of cracks
Structural
- Structural cracks occur due to subgrade settlement and/or stiffness suspension.
- It frequently happens if a floor is over loaded.
Shrinkage
Shrinkage cracks happen once a floor slab dries and will not extend in length, width or number after the completion of drying process.
Reasons for structural cracking
Virtually all structural cracks occur because of subgrade failure.
The failure may happen for one or more of the following factors :-
- The subgrade is design or arranged imperfectly.
- The depth of slab is extremely thin for applied loads and the rigidity of the subgrade.
- The concrete does not contain adequate strength.
It is essential to find out the rigidity of the subgrade and the magnitude of the anticipated loads in order that there is exact slab thickness.
Thickness design of slabs on grade
- Slab rigidity stands for a function of slab thickness.
- Slab cracking strength stands for a function of concrete strength and slab thickness.